Practical 13
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Introduction of
Transmission Media
Transmission media can be defined as physical path between
transmitter and receiver in a data transmission system. Transmission media are
of two types.
Guided
Unguided
Guided: Transmission capacity depends mainly on the medium, the length,
and whether the medium is point-to-point or multipoint (e.g. LAN). Examples are
co-axial cable, twisted pair, and optical fiber.
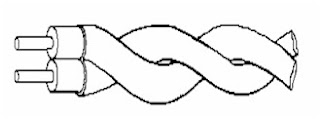
Twisted Pair Cable:
- The oldest, least expensive, and most commonly used media
- The two wires are typically ``twisted'' together in a helix to reduce interference between the two conductors.
- Twisting decreases the interference between adjacent pairs in a cable (two straight parallel wires tend to act as an antenna and pick up extraneous signals.)
- Typically, a number of pairs are bundled together into a cable by wrapping them in a tough protective sheath.
- Can carry both analog and digital signals..
- Quite highly susceptible to noise & interference.
Typical characteristics:
- The data rates upto 1 Mb/s can be achieved for the maximum transmission distance of 1 km.
- For analog voice signals, amplifiers are required about every 6 Km and for digital signals, repeaters are needed for about 2 Km.
- To reduce interference, the twisted pair can be shielded with metallic braid. This type of wire is known as Shielded Twisted-Pair (STP) and the other form is known as Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP).
- Use: Telephone System, Point-to-point, LAN.
Coaxial Cable:
With ``coax'', the medium consists of a copper core surrounded by
insulating material. The insulator is encased by a cylindrical conductor
(copper mesh shield) which is again covered with the plastic protective sheath
(outer insulation).
Coaxial Cable
Co-axial cable has better shielding then twisted pair, so it can
span longer distance at higher speeds. Two types of coaxial cable are widely
used. One kind, 50 ohm cable commonly used for digital transmission and the
other kind , 75 ohm cable commonly used for analog transmission.
Characteristic
of Coaxial Cable
- Most versatile medium
- LANs, Cable TV, Long-distance telephones, VCR to TV connections
- Noise immunity is good
- Very high channel capacity
- Operates at distances up to 100 km (metropolitan area).
- Need repeater/amplifier every few kilometer
Fiber Optics
In fiber optic
technology, the medium consists of a hair-width strand of silicon or glass, and
the signal consists of pulses of light. For instance, a pulse of light means “1'',
lack of pulse means “0”. It has a cylindrical shape and consists of three
concentric sections: the core, the cladding, and
the jacket.
The core, innermost section
consists of a single solid dielectric cylinder. The core is surrounded by a
solid dielectric cladding of refractive index. As a consequence, the light is
propagated through multiple total internal reflections. The core material is
usually made of ultra pure fused silica or glass and the cladding is either
made of glass or plastic. The cladding is surrounded by a jacket made of
plastic. The jacket is used to protect against moisture, abrasion, crushing and
other environmental hazards.
Three components are
required:
1. Fiber
medium: Current technology carries light pulses for tremendous distances (e.g.,
100s of kilometers) with virtually no signal loss.
2. Light
source: typically a Light Emitting Diode (LED) or laser diode. Running current
through the material generates a pulse of light.
3. A
photo diode light detector, which converts light pulses into electrical
signals.
Advantages:
- Very high data rate, low error rate. 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps) over distances of kilometers common..
·
Difficult to tap, which
makes it hard for unauthorized taps as well?
·
Much thinner (per logical phone line)
than existing copper circuits. Because of its thinness, phone companies can
replace thick copper wiring with fibers having much more capacity for same
volume.
- Not susceptible to electrical interference (lightning) or corrosion (rust).
- Greater repeater distance than coax.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Popular posts from this blog
History, Basic Structure, C Token, Data Type, operators, printf() and scanf()
The C Language is developed for creating system applications that directly interact with the hardware devices such as drivers, kernels, etc. C programming is considered as the base for other programming languages, that is why it is known as mother language. It can be defined by the following ways: Mother language System programming language Procedure-oriented programming language Structured programming language Mid-level programming language History of C Language: C programming language was developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at bell laboratories of AT&T (American Telephone & Telegraph), located in U.S.A. Dennis Ritchie is known as the founder of C language . It was developed to overcome the problems of previous languages such as B, BCPL etc. Initially, C language was developed to be used in UNIX operating system . It inherits many features of previous languages such as B and BCPL General Structure...



Newage Cables (Private) Limited is the largest copper wire cable manufacturer of Pakistan and the 1st in its category to be accredited with ISO 9000 certification. Newage was established in 1956 by Mr. Mir Muhammad Azam with the vision of self reliance of a nascent nation and commitment to contribute country’s development by supplying high quality indigenous products to the electrical and industrial infrastructure at competitive rates.
ReplyDelete